This December, skywatchers can enjoy the Geminid meteor shower, which peaks on the night of December 13, and the opportunity to observe asteroid Vesta, especially when it is in opposition. The Moon will also align with planets like Venus, Saturn, and Jupiter on specific dates. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
What are the highlights of sky watching in December 2023? Clear skies will provide a perfect view of the Geminid meteor shower, and you can use your binoculars to look for asteroid Vesta.
Vesta in opposition and Gemini meteors!
The most reliable meteorites of the year are here, without any interference from the bright moon. Gemini peaks overnight from the 13th to the morning of the 14th. And if you want to add “asteroid spotter” to your list of accomplishments, try observing Vesta with binoculars or a small telescope.
Skywatching highlights for December:
- December 7-10 – Catch the crescent moon for weight loss every morning for four days as it rises Venus The bright star, Sunbulah, is in the east during the two hours before sunrise.
- December 12 – new Moon
- December 13 – The Geminid meteors reach their peak last night. Northern Hemisphere observers can look for meteors as early as 9 or 10 p.m., with the number increasing by the hour after midnight. Dress warmly, stay away from bright lights, and enjoy as much of the sky as possible. Meteors will fall all over the sky.
- December 17 – After sunset, look for the crescent moon near you Saturn In the southwest. Binoculars or a small telescope can reveal Saturn’s giant moon Titan as a faint dot next to the planet.
- December 21 – Jupiter It appears almost at full moon in the southeast as darkness falls. Watch them glide across the sky together all night long.
- December 26 – Full moon
- All month long Asteroid Vesta is located in the opposite direction, that is, it is located directly on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun, and at its closest and brightest point for the year. This is a good time to try to view it with binoculars or a small telescope. Look for it to move north in the sky between Gemini and Orion during the month. Use your favorite sky monitoring app to determine its exact location on the night you are observing.
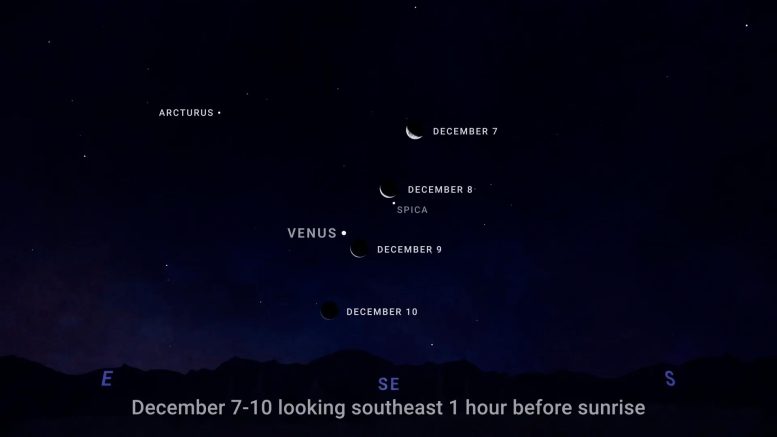
Sky chart showing the crescent moon with Venus on the morning of December 7-10. Image source: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Video version
What’s new for December? Best Views of the Moon and Planets The Geminid meteors are set for a spectacular display, and a chance to observe an asteroid with your own eyes.
The Moon visits the bright planets in the sky, throughout the month, starting four mornings in early December — December 7 to 10 — when you can catch a beautiful array of Venus, the crescent Moon, and the rising. Spica star in the southeast.
Then on the 17th, you’ll find the crescent Moon hanging just below Saturn in the southwest during the first few hours after sunset. Most binoculars will detect both in the same field of view. For a challenge, see if you can see Saturn’s giant moon Titan as a faint dot on the side of the planet here.

A sky chart showing the crescent moon with Saturn on the evening of December 17. Source: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Later that week, the Moon will be nearly full with Jupiter for two nights on the 21st and 22nd. You’ll see them toward the southeast early in the night, traveling west across the sky together throughout the night.
The most reliable meteor shower of the year, the Geminid shower, occurs annually in December. While the Perseid meteors tend to get more attention because they occur during warm weather in the Northern Hemisphere, the Geminid meteors typically produce more meteors. At its peak, you might see a meteor every minute.
The shower reaches its peak overnight on December 13th and the morning of December 14th. Viewers in the Northern Hemisphere can look for meteors as early as 9 or 10 p.m. on the 13th. The number of meteors should increase every hour after that, with the largest number flashing across the sky between midnight and morning twilight.
Skywatchers in the Southern Hemisphere can also see Geminis, although they appear at midnight, and at about a quarter of the northern rate.
If your skies are clear, conditions should be perfect for this year’s peak night, which is just one day after the new moon, leaving the sky nice and dark throughout the night. The meteors appear to radiate from the constellation Gemini, but you’ll see more shooting stars if you look straight up and enjoy as much of the sky as possible.
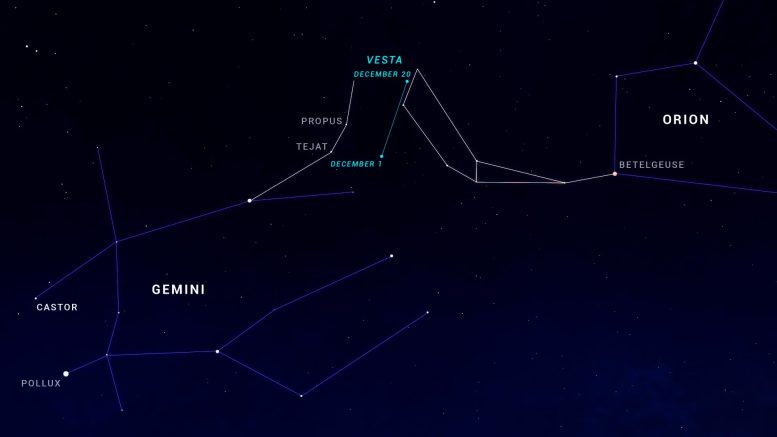
A celestial chart showing the movement of asteroid Vesta during the month of December. Image source: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Do you want to see the asteroid with your own eyes? Asteroid Vesta reaches opposition this month, meaning it is directly on the opposite side of Earth from the sun. This also occurs at the time when Vesta is closest to Earth, so it is brightest and easiest to spot.
Sometimes, Vesta is close enough to the ground in opposition that you can see it with just your eyes. But this year, you’ll need to use binoculars or a small telescope to look for it.
NASAThe Dawn spacecraft came very close to Vesta, orbiting the elliptical globe in 2011 and 2012. She found that Vesta formed in the first two million years of our solar system, and mapped the surface in great detail.
This December, Vesta reaches its highest levels around 1 or 2 a.m. (perfect for telescope viewing), but you can observe it earlier around 10 p.m., when it will appear about halfway up the eastern sky.
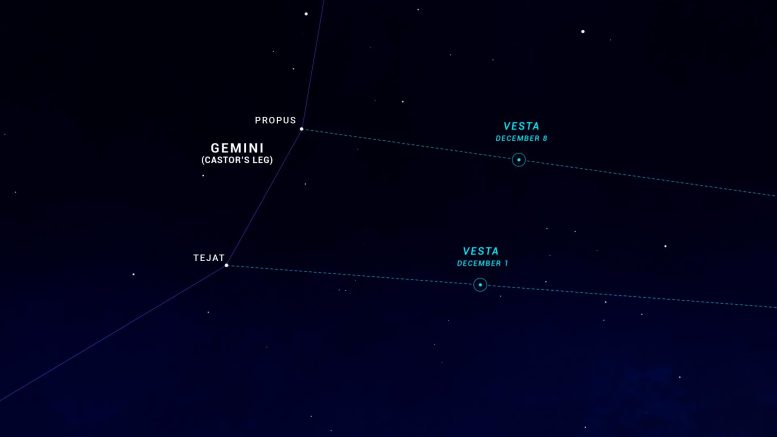
A sky chart showing the position of asteroid Vesta on December 1 and 8. On these nights, Vesta will be easy to find along the line between Orion’s Betelgeuse and one of the two bright stars in Orion. Image source: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Locate Vesta between the rising arm of Orion, here, and Castor’s leg in Gemini, here. On December 1, you can find Vesta along the line between Betelgeuse and this star Tihat. A week later, Vesta moved so that it appeared along this line between Betelgeuse and Probus, here. A pair of simple old binoculars should reveal Vesta about a finger’s width to the west of these two stars. Use your favorite sky-watching app as a guide to Vista’s location within the starfield you see on any given night you’re observing.
And if you’re hungry for more asteroid exploration, there’s more on the way! NASA’s Psyche mission recently set off on its journey to the metal-rich asteroid Psyche, and our Lucy spacecraft just flew by asteroid Dinkinesh and its smaller asteroids at the beginning of November. Lucy heads toward the Trojan asteroids, a unique family of space rocks that share the orbit of Jupiter and are likely remnants of the same primordial material that formed Jupiter and the other exoplanets.
And if that sounds interesting to you, maybe you’re ready to add “asteroid observer” to your list of accomplishments, as you search for Vesta in the December sky.
Below are the moon phases for December.

Moon phases for December 2023. Image source: NASA/JPL-Caltech

“Devoted student. Bacon advocate. Beer scholar. Troublemaker. Falls down a lot. Typical coffee enthusiast.”
